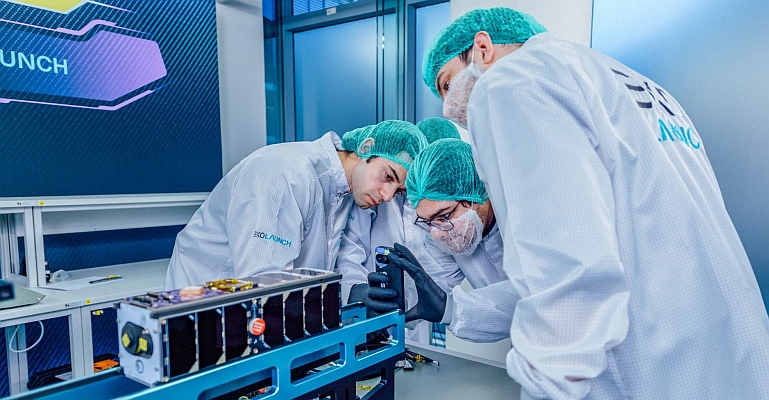
The third and fourth satellites of Europe’s Galileo global navigation satellite system were lofted into orbit on 12 October from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana. They join the first pair of satellites launched a year ago to complete the validation phase of the Galileo programme.

The Soyuz ST-B launcher, operated by Arianespace, lifted off at 18:15 GMT (20:15 CEST) from the Guiana Space Centre. All the stages of the Soyuz vehicle performed as planned and the Fregat-MT upper stage released the Galileo satellites into their targeted orbit at close to 23 200 km altitude, 3 hours 45 minutes after liftoff.
These satellites were built by a consortium led by Astrium as prime contractor, with Thales Alenia Space in charge of assembly, integration and testing. The operations are managed by SpaceOpal a joint company of the DLR German Aerospace Center and Italy’s Telespazio, with the early operations of the satellites controlled by a joint ESA and CNES French space agency team in Toulouse, France.
After initial checks, they will be handed over to the Galileo Control Centres in Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany, and Fucino, Italy, for testing before they are commissioned for the Galileo service validation phase. From a performance point of view, these In-Orbit Validation (IOV) satellites are the same as the forthcoming satellites.
With four identical satellites now in orbit, ESA will be able to demonstrate the performance of the Galileo positioning system fully before the deployment of the remaining operational satellites.
“Since the first launch a year ago, Galileo’s technology has proven itself in orbit,” said Didier Faivre, ESA’s Director of the Galileo Programme and Navigation-related activities. “Thanks to the satellites launched today, the testing phase will be completed, and clear the way for rapid full-scale deployment of the constellation.
“By late 2014, 18 satellites are scheduled to have been launched, by which time early services to Europeans can begin.” Galileo’s Full Operational Capability (FOC) will be reached with 30 satellites (including the four IOVs and in-orbit spares) in 2018.
Source: ESA