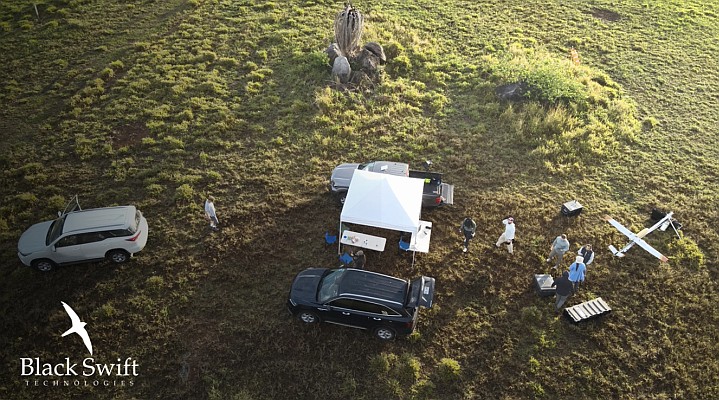
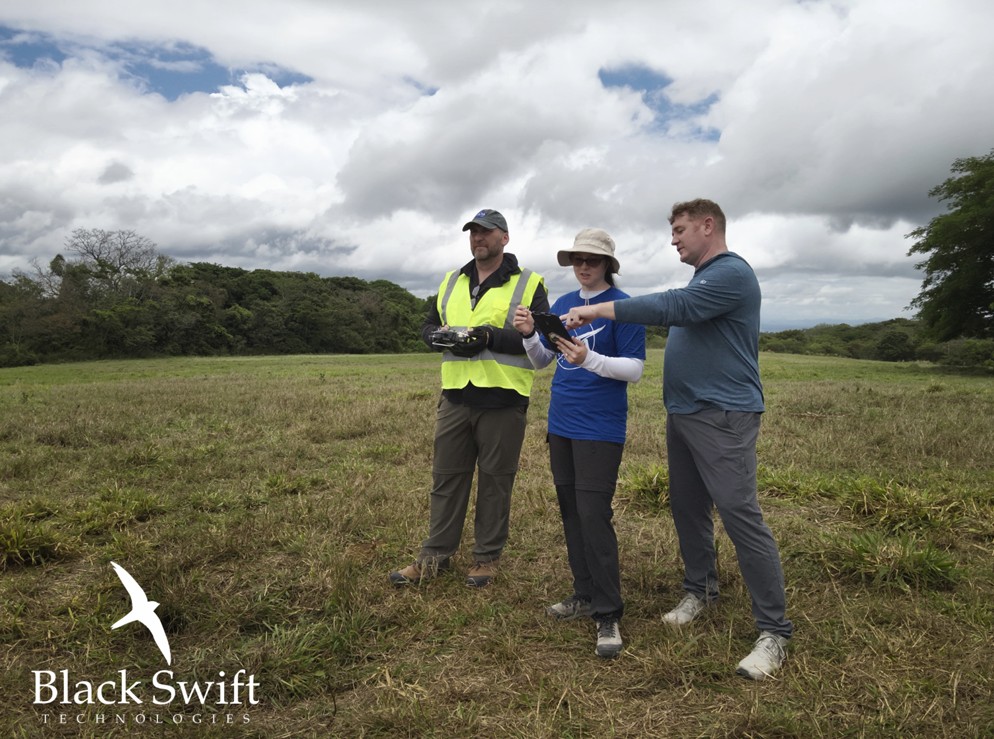
Black Swift Technologies is proud to announce the successful conclusion of the Costa Rica Airborne Research on Forest Ecosystem Response to Volcanic Gas Emissions (CRATER) mission. This groundbreaking scientific field campaign, a vital collaboration led by NASA Ames Research Center in partnership with Black Swift Technologies, and the Universidad de Costa Rica (UCR), leveraged BST’s state-of-the-art Uncrewed Aerial Systems (UAS) to collect high-resolution atmospheric and ecological data. The mission aims to fundamentally advance our understanding of how persistent volcanic gas
emissions influence tropical ecosystems.
The active volcanoes of Costa Rica, including Rincón de la Vieja, Turrialba, and Poás, served as natural laboratories for investigating the long-term exposure of forests to elevated atmospheric CO₂, sulfur dioxide, and hydrogen sulfide. These gases can significantly alter plant health, soil chemistry, and atmospheric dynamics. CRATER aimed to quantify these emissions and assess their spatial and temporal variability by collecting airborne measurements across different terrain features and ecological zones near active volcanic sites.
Central to this campaign was the Black Swift S2 UAS, a fixed-wing, electric-powered aircraft specifically engineered by BST for environmental monitoring in extreme conditions. The S2 is equipped with advanced trace gas sensors, including a LICOR 850 analyzer for CO₂ and H₂O, as well as photogrammetric imaging systems. Its terrain-following autopilot enabled high-resolution sampling of volcanic plumes and surrounding vegetation zones. The S2’s portability and portable catapult launch system provided unparalleled operational flexibility in challenging, remote terrain, allowing launches from diverse sites.
“The CRATER mission has delivered unprecedented data and demonstrated the unparalleled capabilities of our UAS platforms in one of the most demanding environmental monitoring scenarios,” stated a Black Swift Technologies Representative. “Our advanced UAS technology, coupled with the innovative ground station handoff system and sophisticated mission planning tools, allowed us to overcome significant operational challenges, contributing profoundly to Earth system science and setting new benchmarks for autonomous environmental research.”
The CRATER field campaign involved meticulous planning and execution, encompassing extensive pre-flight preparations, rigorous airworthiness documentation, and detailed flight plans in compliance with NASA NPR 7900 and SINAC research permit guidelines. A critical aspect of planning was the use of a highly customized mission planning software suite, part of the SwiftCore flight management system. Originally developed during an earlier NASA mission over Makushin Volcano and extensively adapted by Black Swift Technologies for CRATER’s unique requirements. This advanced tool integrated digital elevation models (DEMs) for terrain-following profiles, calculated obstacle avoidance (including vegetation canopy heights), performed line-of-sight (LoS) communication checks, and predicted battery endurance. It was used daily for real-time visualization and collaborative adjustment of flight routes based on weather and terrain, ensuring safe and scientifically robust operations.
As of May 18, 2025, the team had successfully completed five flights, encompassing both full photogrammetric mapping and trace gas data collection missions. The inherent resilience of the Black Swift S2 platform ensured mission success.

Preliminary data collected by the Black Swift S2 includes:
Imagery for detailed 3D terrain models, orthomosaics, and plant health maps.
In-situ CO₂ concentration profiles, revealing emission gradients consistent with known volcanic vent locations. Preliminary analysis of the trace gas payload data has shown promising stability and reliability, capturing scientifically meaningful variations in CO₂.
Furthermore, Black Swift Technologies played a pivotal role in capacity building, implementing a comprehensive multi-day training program that enabled NASA Ames and partnering institutions to become fully proficient in managing all aspects of UAS mission planning, execution, and post-flight data processing. This “learn-by-doing” approach, overseen by experienced BST personnel, ensured that critical operational knowledge was transferred, fostering long-term independent deployment capabilities for future field campaigns.
The insights gained from the CRATER mission will not only advance UAS-based techniques for monitoring geophysical processes and ecosystems but also inform future rapid-deployment protocols and improve autonomous operations in complex terrain. Ultimately, this research, empowered by Black Swift Technologies’ cutting-edge platforms and expertise, will support long-term goals in global carbon cycle research, volcanic hazard monitoring, and biosphere-atmosphere modeling, providing invaluable contributions to Earth system science.
Source: Black Swift
MundoGEO organizes the DroneShow, MundoGEO Connect, SpaceBR Show and Expo eVTOL exhibitions annually in São Paulo, Brazil. See the highlights of the latest edition: