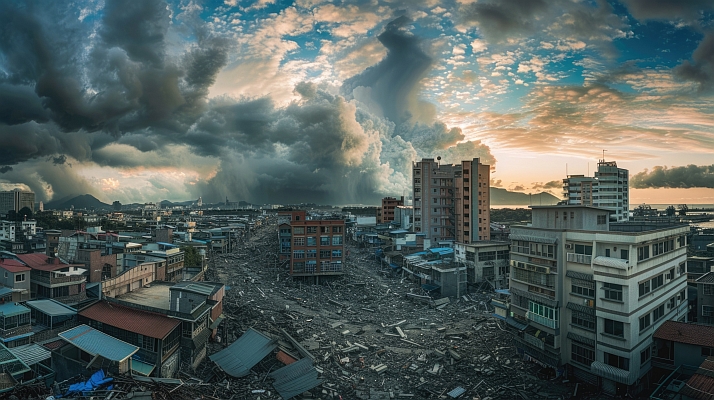
Taiwan, highly exposed to natural disasters, has transformed its disaster management through the Taiwan National Federated Research Data Repository. Powered by the datacube engine rasdaman, this platform integrates satellite imagery, UAV data, and IoT sensor streams across agencies, overcoming long-standing silos. By enabling real-time AI analytics, 3D flood simulations, and secure inter-agency data sharing, it enhances national resilience and supports evidence-based decision-making.
Taiwan’s geographical vulnerability to typhoons, landslides, floods, and earthquakes has long required effective disaster management. Historically, government agencies collected and stored Earth observation data in isolated silos, preventing timely sharing and reducing interoperability. This fragmentation hampered rapid decision-making during emergencies. To overcome these limitations, Taiwan launched a national federated data infrastructure under the leadership of the National Center for High-Performance Computing (NCHC), supported by academic and public partners. At the core of this initiative stands rasdaman, the pioneering datacube engine, which provides the technological backbone for integrating, storing, and analyzing vast spatio-temporal datasets.
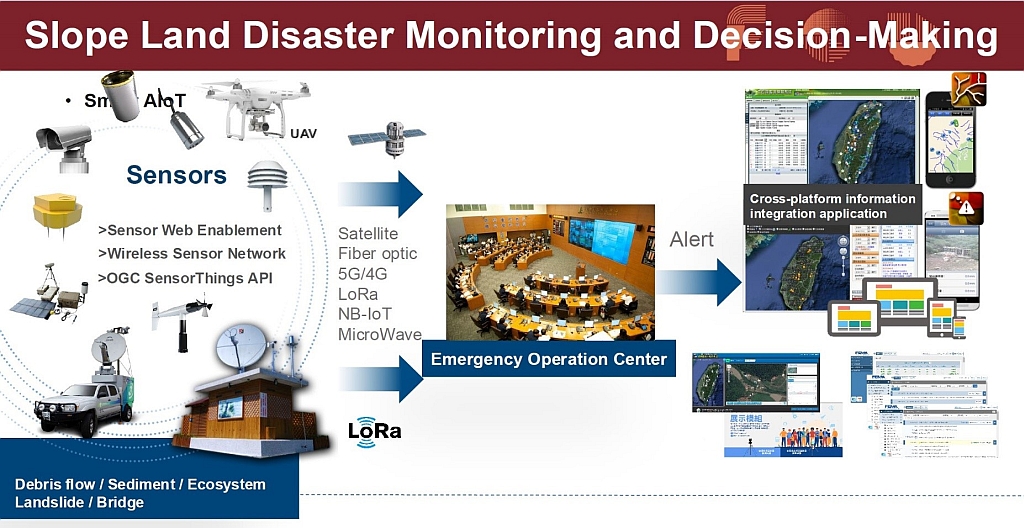
The Taiwan National Federated Research Data Repository enables agencies to share and access multi-source geospatial information, including satellite imagery, UAV data, and IoT sensor streams, through a common, high-performance platform. By offering this service, agencies avoid maintaining costly stand-alone systems, while benefitting from interoperability, scalability, and secure access. Precise access controls allow data providers to determine whether information remains private, conditionally shared, or publicly accessible. A Mandarin-language interface and user-friendly ingestion tools further ensured widespread adoption across technical and non-technical staff.
The datacube technology integration of rasdaman has also facilitated advanced applications. Real-time AI models monitor flood zones by analyzing camera feeds, while UAV thermal imagery combined with 3D GIS simulations helps predict flood dynamics more accurately. These applications incorporate both natural and urban features, enabling authorities to design timely interventions. The repository has been extended to multiple domains: mining oversight, agricultural monitoring, environmental compliance, and academic research.
Although initial resistance emerged regarding data security and unfamiliar technologies, consistent demonstrations, training, and localization measures built trust. Today, the rasdaman-driven system is central to Taiwan’s national spatial data infrastructure, enhancing disaster resilience, supporting evidence-based policymaking, and fostering sustainable urban and environmental governance and infrastructure planning.
Learn more in a case study: https://rasdaman.com/Case-Studies/Case-Study_Taiwan_en.pdf
Source: Rasdaman
MundoGEO organizes the DroneShow, MundoGEO Connect, SpaceBR Show and Expo eVTOL exhibitions annually in São Paulo, Brazil. See the highlights of the latest edition: